By Database Experts at dbsnOOp


Most expensive incidents in production environments start in the database: that is where latency, locks, and wasted resources accumulate. Therefore, they remain the most critical component of the infrastructure and, at the same time, the most fragile. While stateless applications in containers can be restarted or horizontally scaled in seconds, the database carries the weight of state, consistency, and persistence.
For any senior DBA, DevOps, or SRE professional, the default configuration of a my.cnf file is only the first part of a long journey. Optimizing a MySQL or MariaDB environment is not an “install and forget” process; on the contrary, it is dynamic and requires fine-tuning against a moving target: the volatile performance of an environment in the process of scaling or updating. The exponential growth of data volume, the architecture of distributed microservices, and the demand for “five nines” (99.999%) availability have made traditional approaches obsolete.
Management that waits for the “high CPU consumption” alert or a “slow system” ticket is no longer acceptable. The cost of downtime and latency is measured in direct loss of revenue and reputation.
Given this context, we wrote a technical article to address the main performance themes in MySQL and MariaDB. We will explore human limitations in manual tuning and demonstrate how AI and predictive observability are redefining data engineering, transforming performance management into an exact and autonomous science.
1. Performance in MySQL (InnoDB)
For the vast majority of workloads, performance in MySQL centers on InnoDB. Understanding how this storage engine manages memory and disk is the first step for any serious optimization. The ultimate goal is always the same: reduce physical I/O (disk) and maximize logical I/O (memory).
Advanced Buffer Pool Management
innodb_buffer_pool_size is undoubtedly the most critical variable. It acts as a cache for data and indexes. The popular golden rule suggests allocating “70-80% of physical RAM” on dedicated servers. However, in high-performance engineering, general rules are dangerous.
An oversized Buffer Pool in a system with high concurrency can lead to memory swapping at the operating system level, which is catastrophic for database performance. Conversely, an undersized pool forces page thrashing, where InnoDB spends excessive cycles reading and discarding pages from disk.
Data-Driven Technical Validation:
Validation requires measurement over assumptions. To determine the actual effectiveness of your memory allocation, you must calculate the Cache Hit Ratio.
-- Buffer Pool Efficiency Diagnosis Query
SHOW GLOBAL STATUS LIKE 'Innodb_buffer_pool_read%';
/*
DATA INTERPRETATION:
Innodb_buffer_pool_read_requests = Total logical reads (requested by the engine).
Innodb_buffer_pool_reads = Total physical reads (that were not in memory and went to disk).
*/
The efficiency formula is:
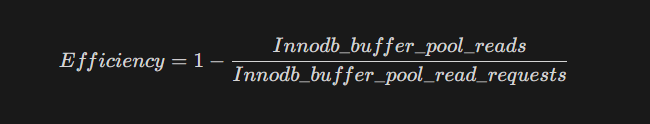
In optimized production environments, this value should be greater than 99.9%. If your monitoring indicates 95% or less, your system is bound to disk performance (I/O Bound), which introduces significant latency.
Redo Log and I/O Capacity
Another frequent and misunderstood bottleneck lies in the innodb_log_file_size and innodb_io_capacity variables.
InnoDB uses a Write-Ahead Logging (WAL) architecture. Transactions are written sequentially to the Redo Log before being applied to data files (tablespaces). If log files are too small, MySQL needs to perform aggressive Checkpoint operations, forcing the writing of dirty pages from the buffer to disk to free up log space. This causes “sawtooth” I/O spikes that degrade application performance.
- Fine Tuning: Increasing log size improves write performance, as it allows more data in memory before the flush.
- The Trade-off (MTTR): Larger log files increase the Mean Time To Recovery (MTTR). If the database crashes, InnoDB will take longer to replay the log and recover consistent state.
2. Query Optimization and Indexing
There is no hardware or my.cnf adjustment that saves a poorly written query. The biggest performance gains are found when optimizing SQL, often on the order of 10 to 100 times more.
Covering Indexes
Many developers understand the basic index in a WHERE clause. However, experts use Covering Indexes.
When an index contains all the columns requested by a query (in SELECT, JOIN, WHERE, and ORDER BY), the database can retrieve the results by reading only the B-Tree structure of the index, never touching the main table (Clustered Index). This saves massive random I/O operations.
Technical Case Study:
Imagine an orders table with millions of rows.
Problem Query:
SELECT customer_id, total_amount, order_date
FROM orders
WHERE status = 'shipped'
ORDER BY order_date DESC;
If there is an index only on status, MySQL will filter, but it will have to perform a lookup in the main table to fetch total_amount and order_date for each found row, and then perform a filesort to order.
Solution with Covering Index:
CREATE INDEX idx_covering ON orders (status, order_date, customer_id, total_amount);
With this composite index, MySQL executes the entire query just by traversing the index. The EXPLAIN will show Using index in the Extra column, the “Holy Grail” of SQL optimization.

Execution Plans (EXPLAIN)
Correctly reading EXPLAIN is the skill that separates juniors from seniors.
- type: ALL: Full Table Scan. The database read the entire table. Acceptable in tiny tables, disastrous in large volumes.
- type: index: Full Index Scan. The database read the entire index. Better than reading the table, but still slow.
- type: ref / eq_ref: The database used the index to find specific rows. Ideal.
- Extra: Using temporary; Using filesort: Critical indicators of degradation. The database needed to create temporary structures on disk to resolve the query.
3. Connections in Sleep State
So you have problems with inactive connections, right? They used to be called annoying connections.
First, we have the max_connections variable. This is the limit of manageable connections your server will make. If you define max_connections as 100, for example, no connection above the 100th will be allowed. If the server keeps open those that are never used again, this is a problem to be addressed.
Many database connections typically indicate that the application is flawed or that the application was not well designed. Very specific applications actually need to open several. Come on! Use connection pools for God’s sake!
Remember that each inactive connection has a minimum resource consumption, such as memory. Minimum memory consumption per connection is about 192 KB to 256 KB, but this depends on what happens when the connection is closed.
What can lead to a connection in sleep state?
- Inadequate handshaking;
- Network failure;
- Application failure;
- Manager failure;
- Programming mistake.
If you notice many connections in sleep state on your MySQL server, it is necessary to dedicate some time to investigate. dbsnOOp offers ways to track them and useful tools to combat inactive ones.
4. MariaDB and Distributed Systems Complexity
MariaDB has evolved beyond a simple branch or spin-off of MySQL. With the introduction of Galera Cluster, it offers synchronous multi-master replication, which brings real high availability but introduces a new class of performance challenges.
Galera Cluster
Unlike traditional asynchronous MySQL replication (Source-Replica), where lag (seconds_behind_master) is tolerated, Galera ensures strict consistency. However, the CAP theorem reminds us that consistency and availability in network partitioning have a price: latency.
Flow Control
In the case of a synchronous cluster, the cluster’s write speed is defined by the slowest node. If a node (Node C) is suffering from high CPU load or slow disk, it will not be able to apply writesets at the same speed as other nodes.
To avoid inconsistency, Galera activates the Flow Control mechanism. The slow node sends a signal to pause replication on all other nodes.
- Symptom: The application experiences intermittent “freezes” in writes, even if other database nodes are idle.
- Diagnosis: Monitor the variable wsrep_flow_control_paused. If this value is greater than 0.0, your cluster is being throttled by a sick member.
Concurrency and Certification Failures
In multi-master architectures, simultaneous writes on the same row in different nodes result in conflict. Galera resolves this through Optimistic Certification (optimistic rollup): the first transaction to reach the commit stage wins, while the other transaction receives a Deadlock error and is aborted.
Monitoring wsrep_local_cert_failures is essential. A high number indicates that the application architecture is not optimized for multi-master (“Hot Rows”), requiring refactoring or load partitioning.
5. The Human Limit
So far, we have discussed deep manual techniques. The problem is that, at current scale, manual application of these techniques is unfeasible.
- You cannot monitor wsrep_flow_control_paused 24/7.
- You cannot review the EXPLAIN of every new query introduced in every microservices deploy.
- You cannot manually correlate I/O spikes with user behavior changes in real-time.
This is where Platform Engineering meets Artificial Intelligence. Tools like dbsnOOp are not just dashboards; they are Predictive Observability systems.
Dynamic Baselines
Traditional monitoring alerts if CPU passes 90%. dbsnOOp’s AI learns your database’s “normal” behavior: if CPU hits 50% at 3 AM (when it should be 5%), this is a serious anomaly, perhaps a data leak or a phantom job. Traditional monitoring would ignore this while AI alerts because it understands context and seasonality.
Automated Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
When an incident occurs, Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) is the most important metric. A human takes time to log into VPN, open terminal, run top, enter MySQL, verify processlist, check error log, and correlate data.
dbsnOOp’s Copilot does this instantly. It correlates:
- Application performance degradation.
- With a Lock Wait spike in the database.
- Identifies the exact query (SQL_ID) causing the block.
- Identifies who executed it (User/Host).
- Suggests the action (e.g., KILL QUERY or create index).
Instead of saying “The database is slow,” the AI says: “Query X is blocking table Y, causing queue in Galera Cluster and raising Payment API response time by 400%.”
Proactive Optimization
The high volume of queries executed per second (QPS) in a production environment makes manual analysis of every SQL command unfeasible. In general, standard monitoring tools generate “Top Queries.” However, knowing which query is slow represents only half the work in MySQL optimization.
In this context, dbsnOOp integrates prescriptive Artificial Intelligence. Upon detecting a query degrading performance, the system not only displays it on a dashboard but also analyzes the execution plan (EXPLAIN). The AI identifies, for example, that a query performs a full table scan on a table with millions of records due to the absence of a composite index. The tool then prescribes the solution—”Create index X on column Y”—and offers an optimized version, ready to be copied, pasted, or executed directly by the platform. Furthermore, dbsnOOp waits for the most appropriate moment to apply the fix without compromising MySQL environment stability.
Necessary Evolution
Guaranteeing operational efficiency is a key factor in MySQL and MariaDB management. The variables are many, complexity is high, and the speed of change is relentless.
Trying to manage modern databases only with manual scripts and human intuition is an unacceptable operational risk. The union of deep knowledge about internal database architecture (InnoDB, Galera, Indexing) with the power of dbsnOOp’s Artificial Intelligence creates a powerful synergy.
This frees senior engineers from repetitive “firefighting” tasks and allows them to focus on architecture, innovation, and data strategy.
Don’t wait for the next incident to expose your monitoring’s weaknesses. Elevate your operational maturity.
Schedule a demo here.
Learn more about dbsnOOp!
Learn about database monitoring with advanced tools here.
Visit our YouTube channel to learn about the platform and watch tutorials.

Recommended Reading
- SRE for Databases: Practical Implementation Guide (DBRE): Understand the evolution of the role from DBA to Database Reliability Engineer. This practical guide discusses how to apply SRE principles to the data layer, focusing on automation, SLOs, and collaboration with development teams.
- Performance Tuning: How to Increase Speed Without Spending More on Hardware: Before approving an instance upgrade, it is essential to exhaust software optimizations. This guide focuses on performance tuning techniques that allow extracting maximum performance from your current environment, resolving the root cause of slowness in queries and indexes, instead of just remedying the symptoms with more expensive hardware.
- Why relying only on monitoring is risky without a technical assessment: Explore the critical difference between passive monitoring, which only observes symptoms, and a deep technical assessment, which investigates the root cause of problems. The text addresses the risks of operating with a false sense of security based solely on monitoring dashboards.

