

Waking up in the middle of the night to a critical system alert indicating that the database is overloaded is an experience that haunts the routine of many technology professionals. The heart races, the mind switches to emergency mode, and the race against time to restore system stability begins. Every second of downtime can translate into lost revenue, reduced productivity, and, most importantly, the erosion of user trust.
This scenario, unfortunately, is a symptom of an IT approach that has become obsolete. In a world where technology infrastructure has shifted to the complexity of the cloud—with microservices architectures, containers, and distributed databases—the question is no longer whether your system will fail, but rather when and, more importantly, why. The era of simply checking CPU and memory usage is long gone. Today, the real challenge is understanding the root cause of unexpected behavior before it escalates into a catastrophic issue. Additionally, you can dive deeper into the fundamentals of database monitoring in this more comprehensive article.
In this article, we will dive deep into the vital transition toward a more comprehensive approach to monitoring and observability, uncovering why this paradigm shift is the key to stability, security, and success for any modern business. We will explore the essential pillars of true monitoring and observability, the specific challenges the cloud imposes on database management, and finally, we will present a solution that empowers DevOps teams, SREs, and DBAs to stop being firefighters and become proactive system engineers. A complete monitoring and observability strategy is what separates companies that merely react to failures from those that prevent them.
The Illusion of Security: Why Traditional Monitoring and Observability Approaches Have Failed
Many companies invest heavily in monitoring and observability tools that, at first glance, seem robust. They generate colorful dashboards, real-time moving graphs, and alerts that trigger when CPU, memory, or network traffic thresholds are exceeded. However, in a distributed environment, this superficial view can be dangerously misleading.
Imagine the following scenario: a customer complains about slowness in your e-commerce application. You access your monitoring and observability dashboard, and all the infrastructure metrics appear “normal.” CPU is at 30%, memory at 50%, and no I/O spikes are detected. What traditional monitoring and observability approaches don’t tell you is that, behind those stable numbers, a single poorly optimized query is consuming 90% of the database resources, creating a bottleneck that impacts hundreds of queued transactions.
The monitoring system showed the symptom (slowness) but not the disease (the problematic query). Additionally, check out in this article a case of a problematic query that nearly brought down an entire e-commerce operation.
This is the major flaw of a reactive monitoring and observability approach: it operates like an alarm system that only shouts “Fire!” after the house is already in flames. It tells you what happened but doesn’t provide the vital context to understand why it happened. In an environment with dozens or hundreds of microservices, this lack of context creates an impenetrable “black box.” You see the input and output of data but have no idea what happens in between. The shift to an end-to-end monitoring and observability approach is the only way to illuminate this “black box.”
The hidden cost of not having an effective monitoring and observability strategy is enormous and manifests in several ways, most of which remain invisible to traditional monitoring dashboards.
- Unexpected Load Spikes: A successful marketing campaign can generate an unprecedented volume of traffic, overloading the database and dragging down performance. Without a monitoring and observability platform that correlates traffic spikes with database behavior, your team wastes valuable time chasing the root cause.
- Slow Queries: A developer may introduce a new feature with a query that doesn’t use indexes correctly. This “killer query” may perform well in low-load testing, but in production, it consumes excessive resources and locks the system. Traditional monitoring fails to identify which specific query is causing the issue, turning optimization into an unproductive treasure hunt.
- I/O Bottlenecks: Disk or network issues in your cloud infrastructure directly affect read/write speed. Without precise correlation between infrastructure metrics and database behavior, the SRE may get lost in troubleshooting, blaming the cloud when the real culprit could be a poorly written query.
- Deadlocked Transactions: Conflicts between transactions causing mutual locks can paralyze critical parts of the application. Without detailed visibility into active transactions and locks, the DevOps team is blind—unable to resolve the problem and restore availability. A robust monitoring and observability system must be able to alert you to these events instantly.
- Handling these scenarios reactively, without the necessary context, is unsustainable. A traditional monitoring and observability strategy, focused only on high-level metrics, merely shows that something is wrong. A complete monitoring and observability approach gives you an X-ray view—showing exactly what is happening, why, and how to resolve it.

The Turning Point: The Holistic Approach to Monitoring and Observability
A true monitoring and observability system represents the next level of maturity in systems management. It doesn’t settle for simply showing what is happening—it gives you the power to understand the why deeply and instantly. It’s the difference between seeing a warning light on a car’s dashboard and having access to the full diagnostic report from the engine’s electronic control unit.
This holistic vision is built on three essential pillars that, when intelligently correlated, provide a complete picture of a system’s health and behavior. The synergy between these pillars is what truly defines a comprehensive monitoring and observability approach. To delve deeper into this topic, read our article on the Holistic Approach to Monitoring and Observability.
Pillar 1: Metrics — The “What” and the “When”
Metrics are the foundation of monitoring and observability, especially in a cloud environment. They are the quantitative, measurable data from your applications and infrastructure.
- Infrastructure Metrics: CPU usage, memory, disk I/O, network traffic. Essential, but not sufficient. A CPU at 80% could be caused by a normal load spike—or by a single failing piece of code. Traditional monitoring tools stop here, but an advanced approach takes the next step: correlation.
- Application Metrics: Response time, error rate, throughput. These give visibility into application health, but the root cause of high latency might lie in a component of a distributed service, a third-party API, or—most often—the database.
- Database Metrics: Query latency, connection usage, transaction lock times, cache statistics. These are the most critical for understanding database behavior. An advanced monitoring and observability strategy correlates these metrics with application metrics to pinpoint the exact bottleneck.
Pillar 2: Logs — The “How” and the History
Logs are the records of discrete events. They tell the detailed story of what happened in your system, with timestamps, error messages, and event traces.
- Structured vs. Unstructured Logs: Unstructured logs (the traditional free-text format) are hard to search and analyze at scale. Structured logs (such as JSON) are the key to automation and fast search. A cutting-edge monitoring and observability system treats logs as high-cardinality data, enabling complex queries and aggregations.
- Log Correlation: In a cloud microservices environment, a single request can generate logs across dozens of services. Manually correlating these logs is a nightmare. An intelligent monitoring and observability platform automates this correlation, connecting the full journey of a request across services and databases—crucial for effective observability.
Pillar 3: Traces — The “Where” and the “Through Where”
Distributed traces are the backbone of a complete monitoring and observability system. They map the entire journey of a single request across the distributed system—from frontend to database and back. This is even more critical in a cloud architecture with multiple services and APIs.
- The Request Path: A trace shows the order in which services were called, how long each took to respond, and where an error or bottleneck occurred. It works like a GPS, showing the real-time path of your request across the cloud. Without traces, monitoring and observability become impossible.
- Pinpointing the Problem: If your application is slow, a trace takes you directly to the specific service—or even the exact database query—causing the slowdown. Without traces, DevOps would have to dig through logs from dozens of services to find the culprit. Tracing is the pillar that ensures true end-to-end observability.
With these three interconnected pillars, DevOps and SREs stop being “firefighters” and become “system engineers.” They can not only detect problems but also identify root causes in minutes, not days. This approach to monitoring and observability is what enables resilience and continuous innovation.
The Direct Impact of Monitoring and Observability on Your Operations
A well-implemented monitoring and observability strategy is a competitive advantage that directly impacts the daily work of those managing infrastructure and code, optimizing teams’ time and energy.
For DBAs and Data Engineers: The End of the “Guessometer”
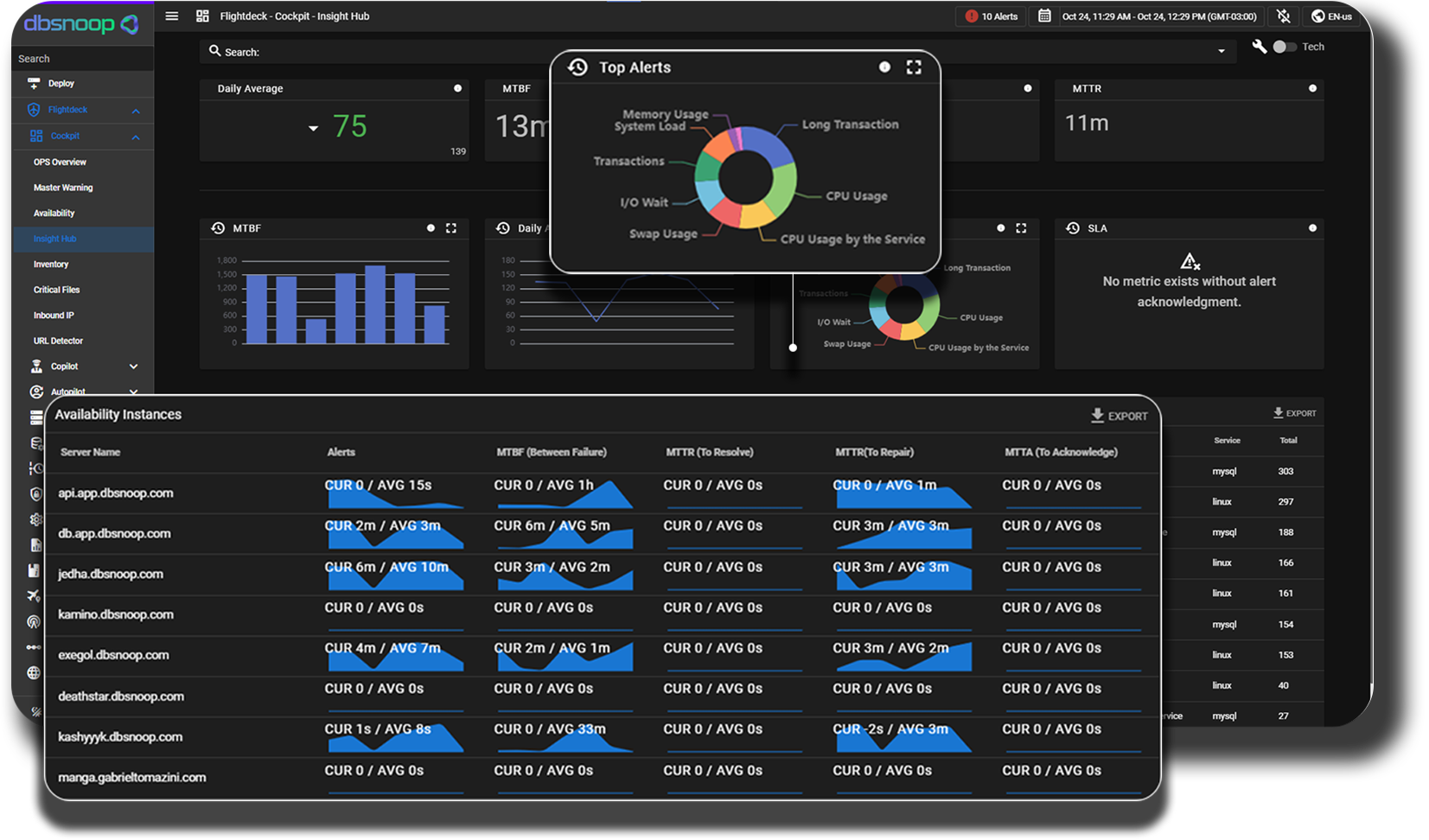
The DBA is the guardian of data. In a world where data is the most valuable asset, database performance is their highest responsibility. A monitoring and observability system empowers the DBA to be proactive rather than reactive.
- Proactive Query Optimization: Instead of waiting for a customer complaint, the DBA can use a monitoring and observability tool to identify queries that are slowing down, even under low workloads. They can analyze execution plans, suggest new indexes, and optimize code before the issue reaches production.
- Capacity Analysis: A monitoring and observability platform provides historical data on database behavior. The DBA can predict database growth and plan hardware upgrades or migrations intelligently and in advance, avoiding performance surprises in the cloud.
- Connection and Pool Management: Understanding active connection usage, deadlocks, and table locks is crucial for high availability. A specialized monitoring and observability platform offers detailed visibility into these events, allowing the DBA to adjust connection pool configurations and prevent bottlenecks. Cloud services add complexity to connection pool management, making effective monitoring and observability essential.
For DevOps and SREs: Less Toil, More Automation
The role of DevOps and SRE is to build and maintain reliable, scalable systems. A monitoring and observability solution is the tool that makes this mission possible, reducing “toil” and increasing automation capabilities.
- Reducing MTTR (Mean Time to Resolution): This is the most critical KPI for an SRE team. With intelligent monitoring and observability, the time between detecting a problem and resolving it is drastically reduced. Teams spend less time hunting for the cause and more time solving the issue, as smart alerts already provide the necessary context.
- Automation and Incident Response: Advanced monitoring and observability tools integrate with automation and notification systems (PagerDuty, Slack). Alerts not only notify teams of issues but also provide necessary context (exact query, error trace), allowing on-call staff to act quickly without logging into multiple cloud systems.
- Unified Visibility: DevOps manages multiple components, from cloud infrastructure to applications and databases. A monitoring and observability platform that unifies the view of these components into a single dashboard, eliminating the “black box” between application and database, is invaluable. An effective strategy removes the need to switch between multiple tools.
For Tech Leads and Developers: Instant Feedback on Code
DevOps culture emphasizes that developers are responsible for production code. But how can a developer be accountable if they cannot see the impact of their code in a constantly changing cloud environment?
- Accelerated Development Cycle: A robust monitoring and observability approach creates an instant feedback loop. Developers can see the impact of new features on system performance in real time, without waiting for performance reports from DevOps. This allows them to fix issues early in the lifecycle before the cost of correction becomes prohibitive.
- Code Quality: Monitoring and observability tools that link slow queries to the exact source code help developers write high-quality code optimized for production environments, whether on-premises or in the cloud. The concept of integrating monitoring and observability into the development lifecycle is known as Shift-Left Observability.

The Specific Challenge of Database Monitoring and Observability in the Cloud
The transition to the cloud has brought numerous benefits, but it has also introduced new complexities for database management. Although there are many managed cloud services (such as Amazon RDS, Aurora, Google Cloud SQL), they still require a specialized layer of monitoring and observability. Most generic cloud monitoring tools provide a superficial view, focused on infrastructure metrics, while ignoring what truly matters: query behavior, index optimization, and transaction health. Learn more about Monitoring and Observability in the Cloud in this essential Guide for your Database.
Generic monitoring solutions often require enormous manual effort to correlate logs from different systems, making troubleshooting a Herculean task. They treat the database as just another infrastructure component, when in reality, it is the heart of the entire system. If the heart fails, the whole body suffers.
- PostgreSQL Autovacuum: A crucial process for PostgreSQL performance can become a bottleneck if not monitored and adjusted properly. Generic cloud monitoring tools cannot provide insights into autovacuum behavior, its frequency, or its impact on performance—a dangerous blind spot.
- Latency in NoSQL Databases: In databases like MongoDB or Redis, latency can result from misconfigured caches, unbalanced shards, or queries that are not using the correct indexes. Only a specialized database monitoring and observability tool for the cloud can provide this level of insight.
- The Hidden Cost of Manual Troubleshooting: The time your DevOps and SRE teams spend finding the root cause of an issue by analyzing logs and metrics in isolation is one of the largest hidden costs. Every minute spent troubleshooting is a minute lost for innovation. This time translates into lost productivity, team stress, and slower feature release cycles. Lack of context is the main culprit of this inefficiency, and the solution is a robust monitoring and observability system.
The complexity of the cloud demands a new approach to monitoring and observability—one that not only collects data but transforms it into actionable insights.
The Solution to Chaos: dbsnOOp, the Monitoring and Observability Platform with an Autonomous DBA
This is where dbsnOOp comes in. We believe that database monitoring and observability should be intelligent, proactive, and—above all—actionable. Our team of experts, who understand the pain points of DBAs and SREs, built dbsnOOp as the ultimate solution for performance and availability challenges, whether in on-premises, hybrid, or cloud environments.
dbsnOOp is not just another generic monitoring tool. It is your database control tower. It solves problems that other cloud monitoring tools ignore. Learn more in this article about dbsnOOp: the Monitoring and Observability Platform with an Autonomous DBA.
- Deep and Granular Visibility: dbsnOOp goes beyond basic metrics. It accurately diagnoses slow queries, identifies I/O bottlenecks, analyzes execution plans, and detects problematic transactions affecting overall performance. Our platform understands the language of your database—PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQL Server, or NoSQL—delivering essential insights that a simple dashboard could never provide. This depth of analysis transforms reactive troubleshooting into proactive data management.
- Unified View of Your Ecosystem: Say goodbye to dozens of dashboards. With dbsnOOp, you have a complete and unified view of all your databases, regardless of technology or cloud type (private, public, or hybrid), in a single place. This eliminates time wasted switching between tools and consolidates the information that truly matters, supporting a centralized monitoring and observability strategy.
- Contextual and Actionable Alerts: Our alerts are contextual and actionable. They don’t just notify you that something is wrong—they provide the context needed to start troubleshooting immediately: the exact query, execution time, user, and optimization recommendation.
- Automation and Actionable Insights: dbsnOOp doesn’t just show the problem—it suggests the solution. Based on intelligent analysis, it offers clear recommendations to optimize queries and improve system performance, allowing your team to focus on innovation instead of repetitive tasks.
- Simple Implementation and Transparent Pricing: Implementing dbsnOOp is straightforward and takes less than 30 minutes. Our pricing model is transparent, per monitored instance, with no end-of-month surprises—unlike competitors who charge per metric or log, which can generate unpredictable costs, especially in the cloud.
- Technology, healthcare, and e-commerce companies already trust dbsnOOp to scale operations safely and ensure high system availability, avoiding revenue loss and team burnout. Choosing a specialized monitoring and observability platform is the smartest investment a company can make in its infrastructure.
The complexity of the cloud demands a new approach to monitoring and observability. The time to shift from reactive to proactive is now. With dbsnOOp, your DevOps and SRE teams can move out of “firefighting” mode and focus on building the future of your company, regardless of the cloud architecture you use.
Do you want to see dbsnOOp in action and discover how it can revolutionize your application’s performance?
Schedule a demo here.
Learn more about dbsnOOp!
Learn about database monitoring with advanced tools here.
Visit our YouTube channel to learn about the platform and watch tutorials.


